k8s cluster architecture
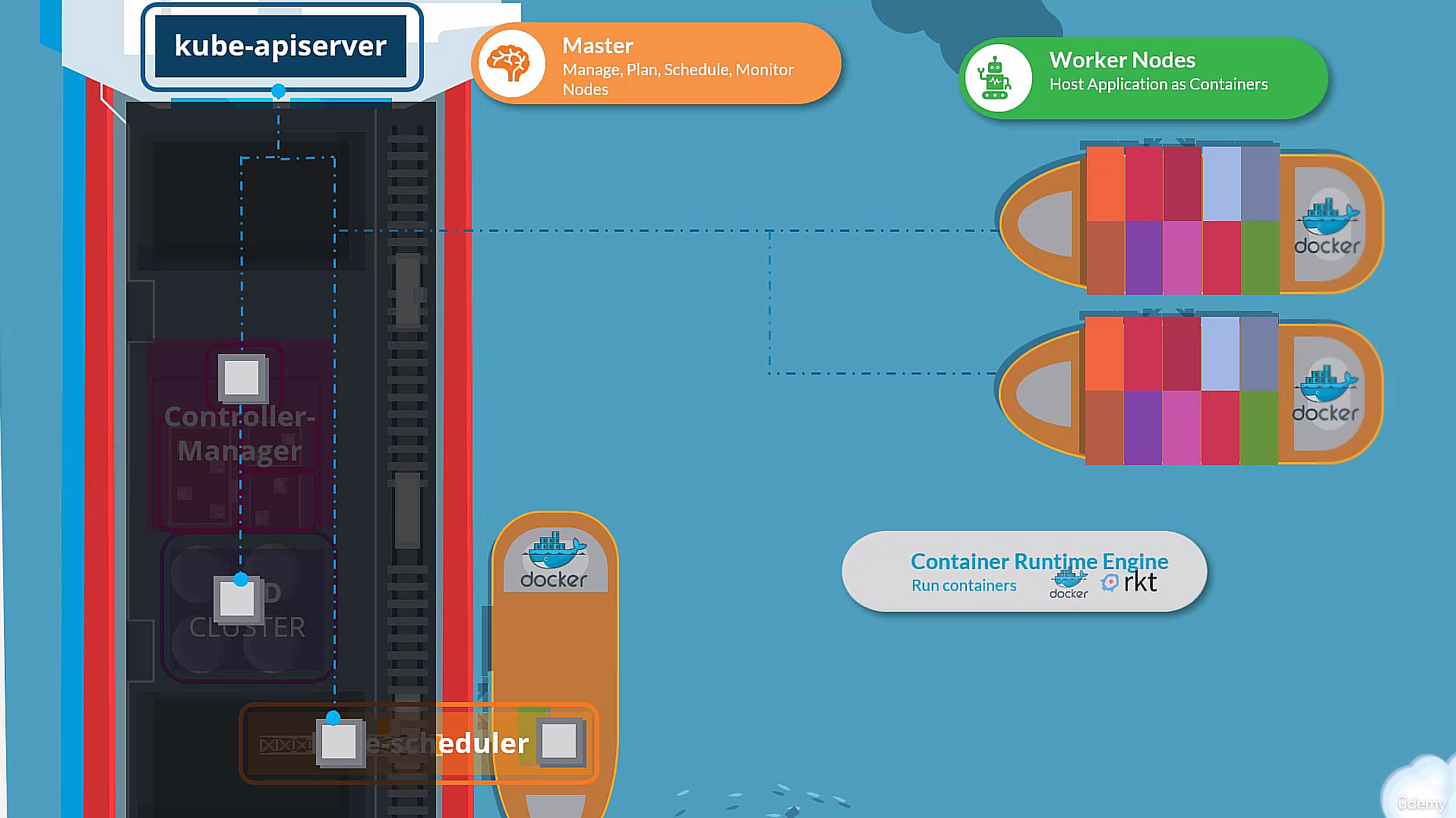 - master nodes: manage the worker nodes and the pods in the cluster - etcd: key-value store for all cluster data - kube-scheduler: schedules pods to worker nodes - kube-controller-manager: runs controller processes - replication controller: ensures that the correct number of pods are running - node controller: monitors the nodes - worker nodes: host the pods that are the components of the application - kubelet: communicates with the master node - kube-proxy: forwards requests to the correct pod
- master nodes: manage the worker nodes and the pods in the cluster - etcd: key-value store for all cluster data - kube-scheduler: schedules pods to worker nodes - kube-controller-manager: runs controller processes - replication controller: ensures that the correct number of pods are running - node controller: monitors the nodes - worker nodes: host the pods that are the components of the application - kubelet: communicates with the master node - kube-proxy: forwards requests to the correct pod
docker vs containerd
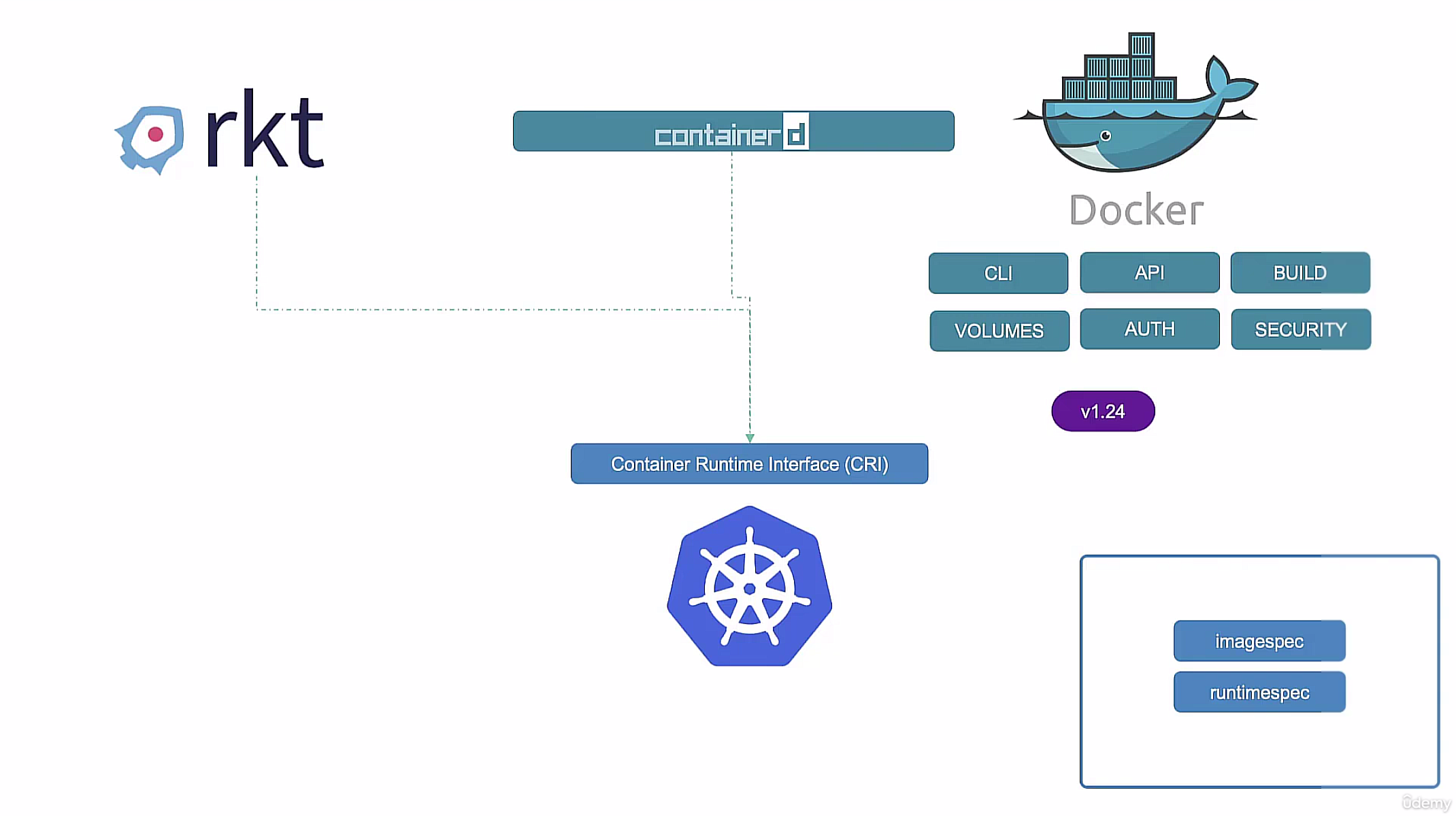
 - initially, k8s was built on top of docker - gradually, k8s started
- initially, k8s was built on top of docker - gradually, k8s started supporting other container runtimes like containerd, cri-o, etc. and built a container runtime interface (CRI) to support multiple container runtimes - docker was not designed to be a container runtime, it was designed to be a container engine so it has a lot of features that are not needed by k8s and removed.
etcd
- key-value store for all cluster data
- stores nodes, pods, configs, secrets, accounts, roles, bindings, etc.
kube-api-server
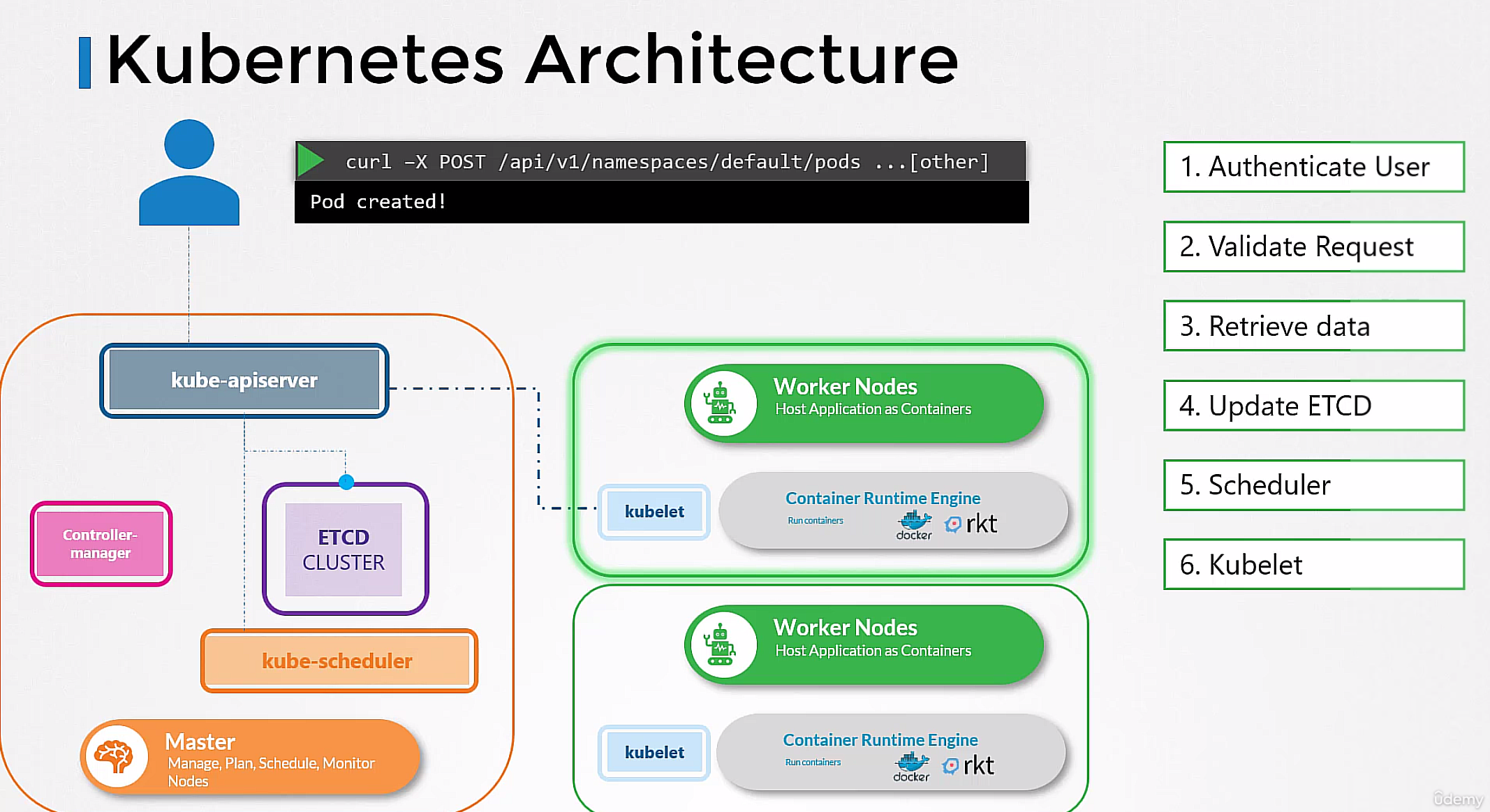
kube-controller-manager
kube-scheduler
kubelet
- must be installed on every node in the cluster
manually## kube-proxy - kubeadm automatically installs kube-proxy on every node using daemonset
- when a service is created, kube-proxy creates a set of iptables rules to forward traffic to the correct pod